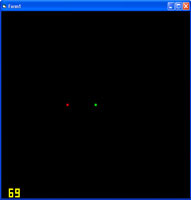
 At present, none of our OpenGL shapes can interact with each other, that is because OpenGL is purely graphics, it doesn't handle physics, so using the Euclidean distance algorithm, we can implement some basic bounding sphere collision ourselves.
At present, none of our OpenGL shapes can interact with each other, that is because OpenGL is purely graphics, it doesn't handle physics, so using the Euclidean distance algorithm, we can implement some basic bounding sphere collision ourselves.OpenGL
 At present, none of our OpenGL shapes can interact with each other, that is because OpenGL is purely graphics, it doesn't handle physics, so using the Euclidean distance algorithm, we can implement some basic bounding sphere collision ourselves.
At present, none of our OpenGL shapes can interact with each other, that is because OpenGL is purely graphics, it doesn't handle physics, so using the Euclidean distance algorithm, we can implement some basic bounding sphere collision ourselves.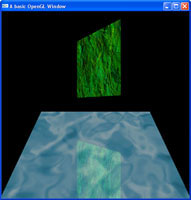 Just like our shadowing tutorial, this one uses the stencil buffer, but we are going to keep our color buffer enabled to allow us to keep our colors for a basic reflection.
Just like our shadowing tutorial, this one uses the stencil buffer, but we are going to keep our color buffer enabled to allow us to keep our colors for a basic reflection. With lighting, comes shadowing. This tutorial takes a basic stencil buffer, and uses it as a stencil to draw a basic shadow on to it.
With lighting, comes shadowing. This tutorial takes a basic stencil buffer, and uses it as a stencil to draw a basic shadow on to it.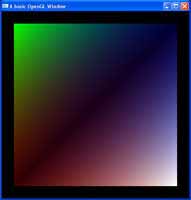 Alpha values, just like colours, can be assigned on a per-vertex basis. This allows for varying levels of transparency across objects.
Alpha values, just like colours, can be assigned on a per-vertex basis. This allows for varying levels of transparency across objects.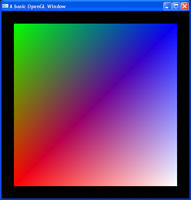 Along with assigning colours to objects, did you know you can also set colours to individual vertices? Well yes, yes you can.
Along with assigning colours to objects, did you know you can also set colours to individual vertices? Well yes, yes you can. The first person camera is done, lets take a look at the third person camera, which is essential any type of Role Playing Game. The best part is, this tutorial uses most of the same code as the previous camera tutorial. Just some minor changes to entirely change the feel of your game.
The first person camera is done, lets take a look at the third person camera, which is essential any type of Role Playing Game. The best part is, this tutorial uses most of the same code as the previous camera tutorial. Just some minor changes to entirely change the feel of your game.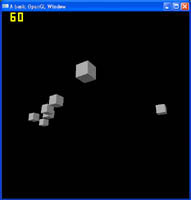 Here I will be extending upon the previous OpenGL Camera tutorial, and adding a strafe feature (moving side to side). A game without strafing, is going to be terrible, especially when it comes to multiplayer when strafing against enemy fire is essential.
Here I will be extending upon the previous OpenGL Camera tutorial, and adding a strafe feature (moving side to side). A game without strafing, is going to be terrible, especially when it comes to multiplayer when strafing against enemy fire is essential.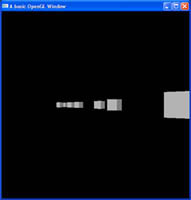 If you look at making any game where the scene is larger than can be displayed in the window at once, then you are going to need some type of camera system. This is the first of several tutorials on building a first person camera system.
If you look at making any game where the scene is larger than can be displayed in the window at once, then you are going to need some type of camera system. This is the first of several tutorials on building a first person camera system.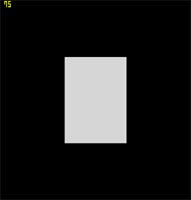 Display lists are a cached version of a set of OpenGL calls, which can be called again and again, at quicker framerates than writing the code over and over again. There is much controversy over the use of these against Vertex Buffer Objects in relation to speed, so I will show you both, starting with display lists in this tutorial.
Display lists are a cached version of a set of OpenGL calls, which can be called again and again, at quicker framerates than writing the code over and over again. There is much controversy over the use of these against Vertex Buffer Objects in relation to speed, so I will show you both, starting with display lists in this tutorial.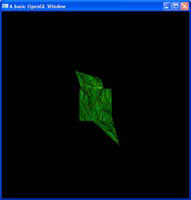 Mip maps are an essential texture extension, which creates scaled down versions of a texture and uses them when an object gets further away, or closer to the near plane. This scaled down version of the texture, makes for nicer, smoother looking textures.
Mip maps are an essential texture extension, which creates scaled down versions of a texture and uses them when an object gets further away, or closer to the near plane. This scaled down version of the texture, makes for nicer, smoother looking textures.